Spatial Decision Support Systems: integrate spatial analytics with business intelligence and maximize your business’s efficiency
Do you know that 80% of your Business Intelligence has a geographic component that remains virtually unexploited with traditional business data analysis systems?
Take advantage of the geographic data of your business
Strategic analysts, almost totally dependent on their organizations’ information systems that usually offer limited or no spatial analysis capabilities are finding it hard to effectively exploit the available spatial information and to implement new market analysis techniques that could greatly improve their organization’s efficiency.
To meet this challenge, a technology for interfacing and / or integrating geographic information system operations into existing business intelligence environments has been developed.
What challenges do you need to meet to achieve this necessary interoperability? Terra, Mapping the Globe can help you
The Importance of Location Information
Failure to connect and / or integrate maps and geographic information systems tools deprives most organizations of the ability to draw useful and necessary conclusions from the spatial analysis of their data.
Organizations over time understand the importance of analyzing geospatial data in their business intelligence and are actively seeking to improve their business insight. Strategic analysts are required to exploit geographical location information to easily understand basic concepts:
- Where are my customers?
- How can I keep my existing clients and attract new ones by improving my distribution network using geography?
- How can my workforce deliver at a higher and more efficient level?
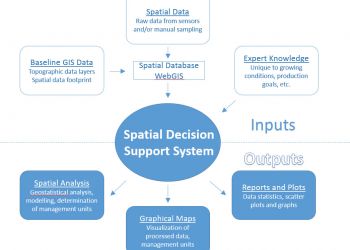
ΒΙ + GIS = Spatial Decision Support System (SDSS)
Business Intelligence (BI): The technique of identifying, extracting and analyzing business data
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): the connection of geographic and descriptive data in space and time
Spatial Decision Support System: the necessary and analytical capability of interconnection and interoperability of spatial and business data
It is necessary for a spatial analysis solution to interoperate and integrate with BI and the Data Warehouse platform of a business in order to provide a powerful tool for geospatial functions such as:
- Digital maps
- Geocoding / reverse geocoding
- Search for addresses and points of interest
- Routing
- VRP
- Service areas calculations
The emergence of service-oriented architectures (SOA) implemented through web services and APIs allows BI systems and analytical tools to communicate freely with each other and with the data warehouse. These architectures also enable the smooth and seamless interconnection and integration of scalable and based on interoperability standards geospatial analysis into a business intelligence system, even in a multi-platform BI environment.
Interoperability is more than just software
- The ability to enable location information in business data offers:
- Data cleansing for optimization of quality and integrity
- Geocoding to accurately determine the geographical coordinates of the location of the data through the address
- Use of corporate or external geospatial data for modeling and analysis
- Calculation of other geospatial functions (routing, VRP, coverage areas, etc.) that offer additional spatial information
- Use of the above spatial information in applications and processes in need
Terra, Mapping the Globe
In this context, our company can prove to be a valuable partner in the following areas:
- Terra GIS API for systems integration
- Implementation of GIS applications development
- Provision of geographic content
- Consulting services (systems integration, database design, managed cloud services)

